一、pandas的安装:
1.安装pandas其实是非常简单的,pandas依赖处理Excel的xlrd模块,所以我们需要提前安装这个,安装命令是:pip install xlrd
2.开始安装pandas,安装命令是:pip install pandas
二、读取excel文件
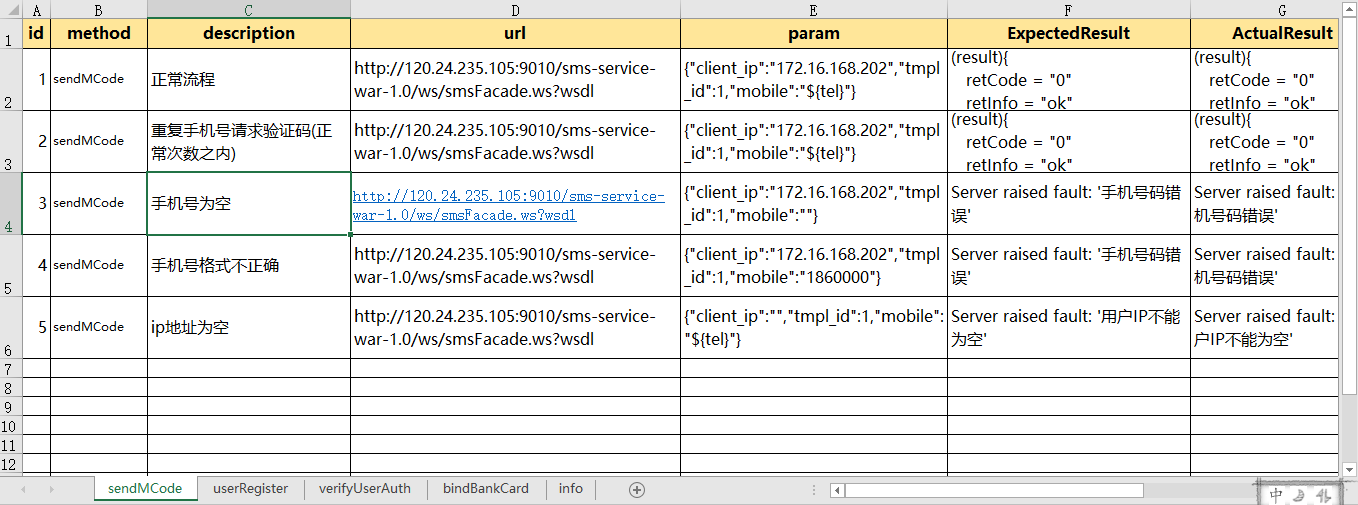
webservice_testcase.xlsx结构如下:
1.首先我们应该先将这个模块导入
import pandas as pd2.读取表单中的数据:
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx')#这个会直接默认读取到这个Excel的第一个表单
data=sheet.head()#默认读取前5行数据
print("获取到所有的值:\n{0}".format(data))#格式化输出 3.也可以通过指定表单名来读取数据
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx',sheet_name='userRegister')
data=sheet.head()#默认读取前5行数据
print("获取到所有的值:\n{0}".format(data))#格式化输出4.通过表单索引来指定要访问的表单,0表示第一个表单,也可以采用表单名和索引的双重方式来定位表单,也可以同时定位多个表单,方式都罗列如下所示
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx',sheet_name=['sendMCode','userRegister'])#可以通过表单名同时指定多个
# sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx',sheet_name=0)#可以通过表单索引来指定读取的表单
# sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx',sheet_name=['sendMCode',1])#可以混合的方式来指定
# sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx',sheet_name=[1,2])#可以通过索引 同时指定多个
data=sheet.values#获取所有的数据,注意这里不能用head()方法
print("获取到所有的值:\n{0}".format(data))#格式化输出二、操作Excel中的行列
1.读取制定的某一行数据:
sheet=pd.read_excel('webservice_testcase.xlsx')#这个会直接默认读取到这个Excel的第一个表单
data=sheet.ix[0].values#0表示第一行 这里读取数据并不包含表头
print("读取指定行的数据:\n{0}".format(data))得到了如下结果:

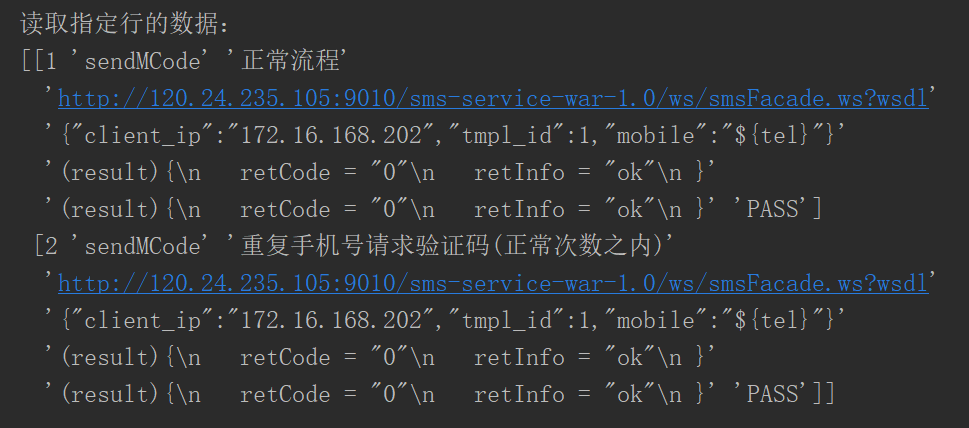
2.读取指定的多行:
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx')#这个会直接默认读取到这个Excel的第一个表单
data=sheet.ix[[0,1]].values#0表示第一行 这里读取数据并不包含表头
print("读取指定行的数据:\n{0}".format(data))得到了如下的结果:
3.读取指定行列的数据:
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx')#这个会直接默认读取到这个Excel的第一个表单
data=sheet.ix[0,1]#读取第一行第二列的值
print("读取指定行的数据:\n{0}".format(data))得到了如下结果:

4.读取指定的多行多列的值:
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx')
data=sheet.ix[[1,2],['method','description']].values#读取第二行第三行的method以及description列的值,这里需要嵌套列表
print("读取指定行的数据:\n{0}".format(data))得到了如下的结果:

5.读取所有行指定的列的值:
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx')
data=sheet.ix[:,['method','description']].values#读取第二行第三行的method以及description列的值,这里需要嵌套列表
print("读取指定行的数据:\n{0}".format(data))得到了如下的结果:

6.获取行号输出:
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx')
print("输出行号列表",sheet.index.values)得到了如下的结果:

7.获取列名输出:
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx')
print("输出列标题",sheet.columns.values)得到了如下的结果:

8.获取指定行数的值:
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx')
print("输出值",sheet.sample(2).values)9.获取指定列的值
sheet=pd.read_excel('test_data\\webservice_testcase.xlsx')
print("输出值",sheet['description'].values)得到了如下的结果:

三、将excel中的每一条数据处理成字典,然后让如一个列表中
test_data=[] sheet = pd.read_excel(self.file_name, sheet_name=key) for i in sheet.index.values:#获取行号的索引,并对其进行遍历:#根据i来获取每一行指定的数据 并利用to_dict转成字典 row_data=sheet.ix[i,['id','method','description','url','param','ExpectedResult']].to_dict() test_data.append(row_data)
另外,我们可以把测试用例相关的东西写入一个配置文件当中,读取的时候可以根据配置文件中的内容来进行读取:
配置文件如下:
[CASECONFIG]
sheet_list={'sendMCode':'all',
'userRegister':'all',
'verifyUserAuth':'all',
'bindBankCard':[]
} 配置文件处理.py代码如下:
import configparser
class ReadConfig:
def read_config(self,file_path,section,option):
cf=configparser.ConfigParser()
cf.read(file_path,encoding="utf-8")
value=cf.get(section,option)
return valueproject_path.py代码如下:
import os Project_path=os.path.split(os.path.split(os.path.realpath(__file__))[0])[0] #配置文件路径 case_config_path=os.path.join(Project_path,'config','case.config') #测试用例的路径 test_cases_path=os.path.join(Project_path,'test_data','webservice_testcase.xlsx')
然后我们把读取excel中的内容封装成一个类,代码示例如下:
from common import project_pathfrom common.read_config import ReadConfig as RC
import pandas as pd
class DoExcel:
def __init__(self,file_name):
self.file_name=file_name
self.sheet_list=eval(RC().read_config(project_path.case_config_path,'CASECONFIG','sheet_list'))
def do_excel(self):
test_data=[]
for key in self.sheet_list:
if self.sheet_list[key] == 'all': # 读取所有的用例
sheet = pd.read_excel(self.file_name, sheet_name=key)
for i in sheet.index.values:#获取行号的索引,并对其进行遍历:
#根据i来获取每一行指定的数据 并利用to_dict转成字典
row_data=sheet.ix[i,['id','method','description','url','param','ExpectedResult']].to_dict()
test_data.append(row_data)
else:
sheet = pd.read_excel(self.file_name, sheet_name=key)
for i in self.sheet_list[key]:#根据list中的标号去读取excel指定的用例
row_data=sheet.ix[i-1,['id','method','description','url','param','ExpectedResult']].to_dict()
test_data.append(row_data)
return test_data
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_data=DoExcel(project_path.test_cases_path).do_excel()
print(test_data)如果将配置改成如下内容:
[CASECONFIG]
sheet_list={'sendMCode':[1,3,5],
'userRegister':[],
'verifyUserAuth':[],
'bindBankCard':[]
} 我们将会得到如下的运行结果:
[{: 1, : , : , : , : , : },
{: 3, : , : , : , : , : },
{: 5, : , : , : , : , : }]到此,将excel中的用例数据读取成为[{key1:value1},{key2:value2},...,{keyn:valuen}]这样的形式已经完毕,但是还有很多东西需要完善,比如用例中完成参数的替换,测试完成后回写测试数据到excel对应的表格中等等内容。
更多Python相关文章,请关注Python自学网。








