
安装
可以通过以下的命令进行安装
conda install pytorch-nightly -c pytorch conda install graphviz conda install torchvision conda install tensorwatch
基于以下的版本:
torchvision.__version__ '0.2.1' torch.__version__ '1.2.0.dev20190610' sys.version '3.6.8 |Anaconda custom (64-bit)| (default, Dec 30 2018, 01:22:34) [GCC 7.3.0]'
载入库
import sys import torch import tensorwatch as tw import torchvision.models
网络结构可视化
alexnet_model = torchvision.models.alexnet() tw.draw_model(alexnet_model, [1, 3, 224, 224])
载入alexnet,draw_model函数需要传入三个参数,第一个为model,第二个参数为input_shape,第三个参数为orientation,可以选择'LR'或者'TB',分别代表左右布局与上下布局。
在notebook中,执行完上面的代码会显示如下的图,将网络的结构及各个层的name和shape进行了可视化。
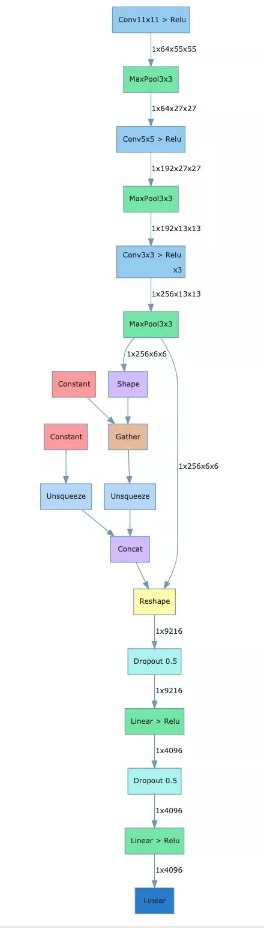
统计网络参数
可以通过model_stats方法统计各层的参数情况。
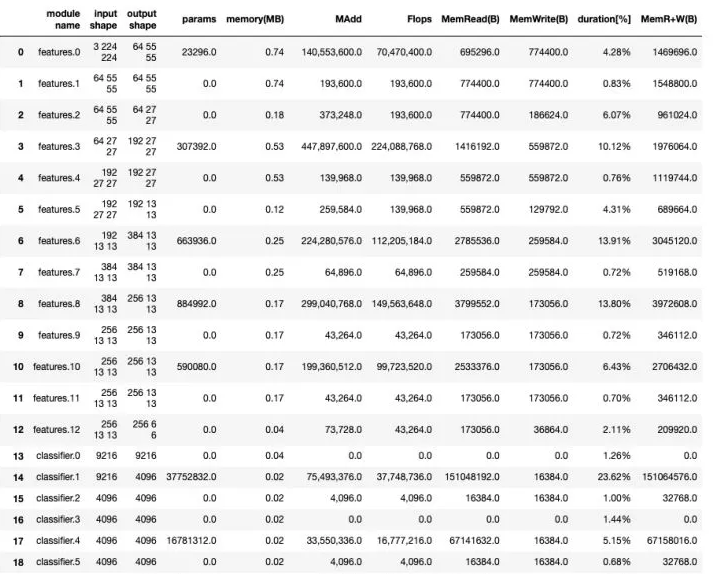
tw.model_stats(alexnet_model, [1, 3, 224, 224]) [MAdd]: Dropout is not supported! [Flops]: Dropout is not supported! [Memory]: Dropout is not supported! [MAdd]: Dropout is not supported! [Flops]: Dropout is not supported! [Memory]: Dropout is not supported! [MAdd]: Dropout is not supported! [Flops]: Dropout is not supported! [Memory]: Dropout is not supported! [MAdd]: Dropout is not supported! [Flops]: Dropout is not supported! [Memory]: Dropout is not supported! [MAdd]: Dropout is not supported! [Flops]: Dropout is not supported! [Memory]: Dropout is not supported! [MAdd]: Dropout is not supported! [Flops]: Dropout is not supported! [Memory]: Dropout is not supported! alexnet_model.features Sequential( (0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(11, 11), stride=(4, 4), padding=(2, 2)) (1): ReLU(inplace=True) (2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) (3): Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) (4): ReLU(inplace=True) (5): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) (6): Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (7): ReLU(inplace=True) (8): Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (9): ReLU(inplace=True) (10): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (11): ReLU(inplace=True) (12): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) ) alexnet_model.classifier Sequential( (0): Dropout(p=0.5) (1): Linear(in_features=9216, out_features=4096, bias=True) (2): ReLU(inplace=True) (3): Dropout(p=0.5) (4): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True) (5): ReLU(inplace=True) (6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000, bias=True) )










