在列表list模块中,已有排序操作方法的实现:
lst = [2,9,5,4,8,1,6] lst.sort() print(lst) # output:[1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9]
如果要自定义实现这一方法呢?
排序一个序列,通常会用到双重(嵌套)循环(双重循环在二维列表、矩阵、行列式中使用比较普通)。
使用双重循环处理一个序列的排序,通常内循环搞定一个元素的位置,外循环搞定一个序列的全部。
排序的方法有很多种,效率及代码难易方面各有千秋。
关于选择排序:
先用一个简单的实例用手动的方式模拟一下实际的操作过程,然后用代码实现一般化。
如数列lst = [2,9,5,4,8,1,6],选择排序操作(升序)如下:
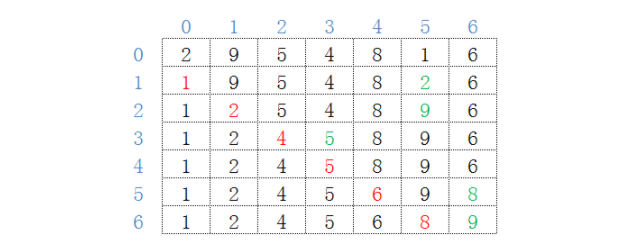
可以描述为:
for i in range(len(lst)-1): .....select the smallest element in lst[i : len(lst)] ....swap the smallest with lst[i], if necessary # lst[i] is in its correct position # the next iteration applies to lst[i+1 : len(lst)]
代码:

output:
[2, 9, 5, 4, 8, 1, 6] [1, 9, 5, 4, 8, 2, 6] [1, 2, 5, 4, 8, 9, 6] [1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 6] [1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 6] [1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 9, 8] [1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9]
关于选择排序内容并不难哦~一串代码就可以演示完成了,小伙伴们浏览几遍即可了解哦~如果还想知道更多的python知识,可以到python学习网进行查询。










