
树的存储、表示与遍历
树的存储与表示
顺序存储:将数据结构存储在固定的数组中,然在遍历速度上有一定的优势,但因所占空间比较大,是非主流二叉树。二叉树通常以链式存储。
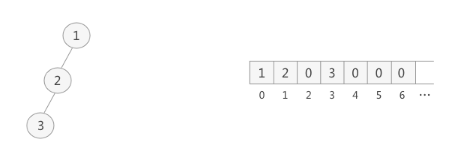
某个节点为空是用0表示。
节点的结构:
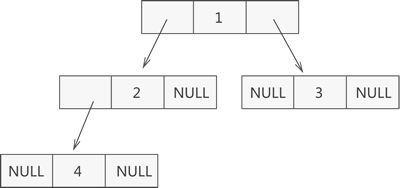
二叉树的建立
class Node(object):
"""二叉树节点的封装"""
def __init__(self, element=None, lchild=None, rchild=None):
self.element = element
self.lchild = lchild
self.rchild = rchild
class Tree(object):
"""二叉树的封装"""
def __init__(self, root=None):
self.root = root
def __add__(self, element):
# 插入节点的封装
node = Node(element)
# 1.判断是否为空,则对根结点进行赋值
if not self.root:
self.root = node
# 2. 如果存在跟结点,将根结点放入队列
else:
queue = []
# 将根结点放入队列中
queue.append(self.root)
# 对队列中的所有节点进行遍历
# 这里的循环每次都是从根结点往下循环的
while queue:
# 3.弹出队列中的第一个元素(第一次弹出的为根节点,然后是根的左节点,根的右节点,依次类推)
cur = queue.pop(0)
if not cur.lchild:
cur.lchild = node
return
elif not cur.rchild:
cur.rchild = node
return
else:
# 左右子树都存在就将左右子树添加到队列中去
queue.append(cur.lchild)
queue.append(cur.rchild)二叉树的遍历
遍历是指对树中所有结点的信息的访问,即依次对树中每个结点访问一次且仅访问一次,我们把这种对所有节点的访问称为遍历(traversal)
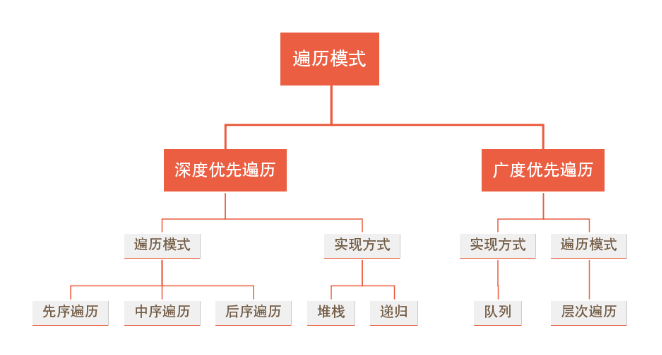
广度优先遍历(层次遍历)
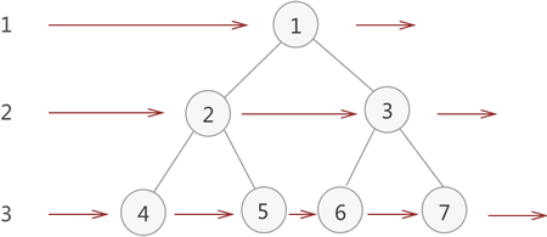
遍历结果为1,2,3,4,5,6,7
def breadth_travel(self):
"""利用队列实现树的层次遍历"""
if self.root == None:
return
# 将二叉树的节点依次放入队列中,通过访问队列的形式实现树的遍历
queue = []
queue.append(self.root)
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
print(node.element, end=',')
if node.lchild != None:
queue.append(node.lchild)
if node.rchild != None:
queue.append(node.rchild)
print()深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历有三种方式:
先序遍历(根->左->右):先访问根结点,再先序遍历左子树,最后再先序遍历右子树,
中序遍历(左->根->右):先中序遍历左子树,然后再访问根结点,最后再中序遍历右子树,
后序遍历(左->右->根):先后序遍历左子树,然后再后序遍历右子树,最后再访问根结点。
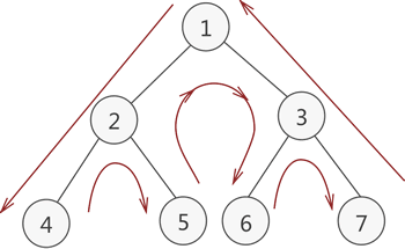
先序遍历: 1 2 4 5 3 6 7
中序遍历: 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
后序遍历: 4 5 2 6 7 3 1
递归实现先序遍历
# 深度优先遍历:先序遍历---根 左 右
def preorder(self, root):
"""递归实现先序遍历"""
if not root:
return
print(root.element, end=',')
self.preorder(root.lchild)
self.preorder(root.rchild)递归实现中序遍历
# 深度优先遍历:中序遍历---左 根 右
def inorder(self, root):
"""递归实现中序遍历"""
if not root:
return
self.inorder(root.lchild)
print(root.element, end=',')
self.inorder(root.rchild)递归实现后序遍历
# 深度优先遍历:后序遍历---左 右 根
def postorder(self, root):
"""递归实现后序遍历"""
if not root:
return
self.postorder(root.lchild)
self.postorder(root.rchild)
print(root.element, end=',')测试代码:
if __name__ == '__main__':
binaryTree = Tree()
for i in range(7):
binaryTree.__add__(i+1)
# 广度优先遍历
print("广度优先:")
binaryTree.breadth_travel()
# 深度优先,先序遍历
root = binaryTree.root
binaryTree.preorder(root)
print('深度优先--先序遍历')
binaryTree.inorder(root)
print('深度优先--中序遍历')
binaryTree.postorder(root)
print('深度优先--后序遍历')广度优先: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7, 1,2,4,5,3,6,7,深度优先--先序遍历 4,2,5,1,6,3,7,深度优先--中序遍历 4,5,2,6,7,3,1,深度优先--后序遍历
和我们预期的结果完全相同。
想了解更多Python知识,请移步Python视频教程继续学习!!











