
Redis简介
Redis是完全开源免费的高性能Key-Value数据库,有以下几个特点:
·Redis支持数据持久化,可以将内存中的数据保存至磁盘中,重启可以再次加载进行使用。
·Redis不仅仅支持简单的Key-Value类型的额数据,同时还提供list,set,zset(有序集合),hash等数据结构的存储。
·Redis支持数据的备份,即master-slave模式的数据备份。
Redis基本操作
1、字符串相关操作
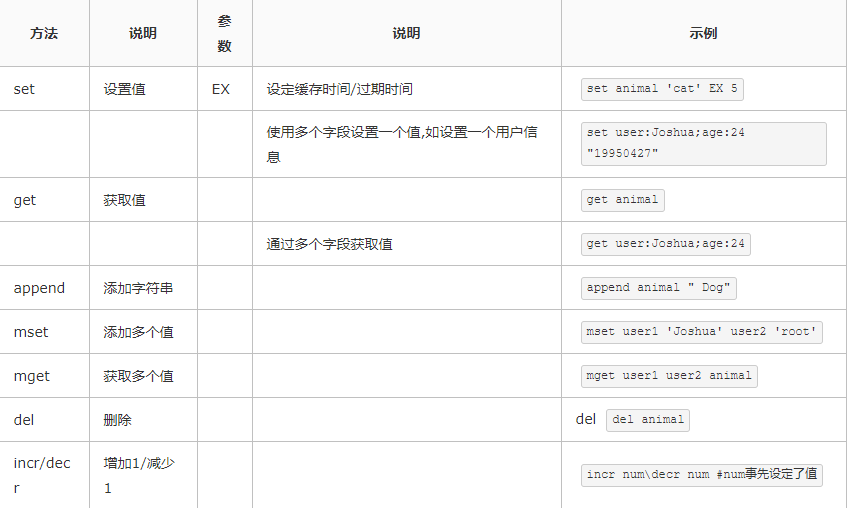
2、列表相关操作
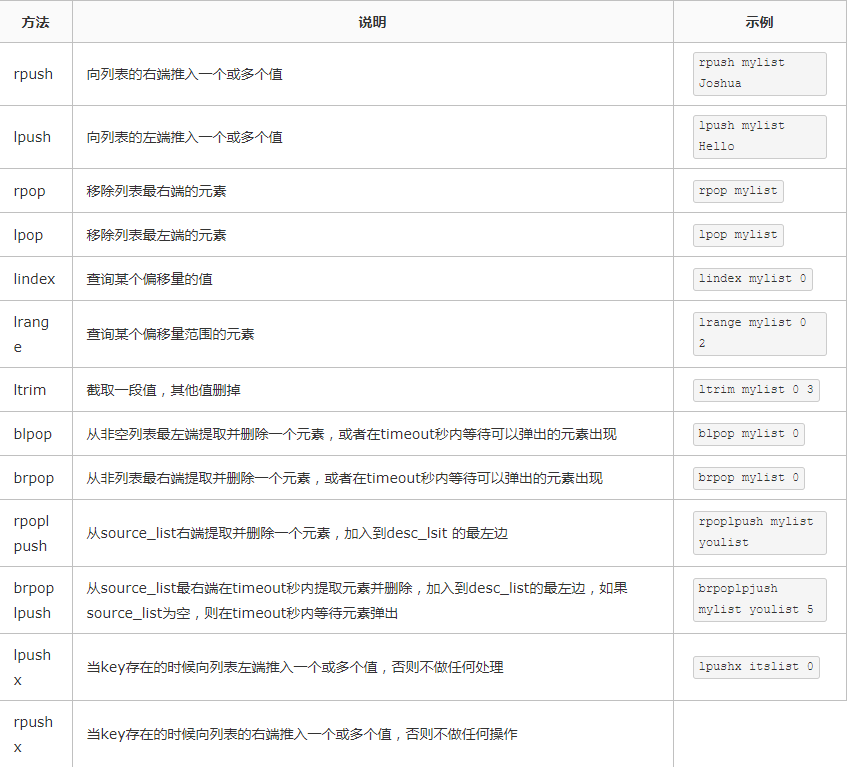
3、集合相关操作
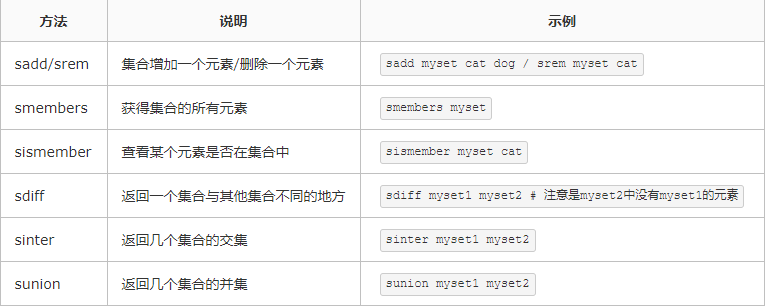
4、散列(hash)操作
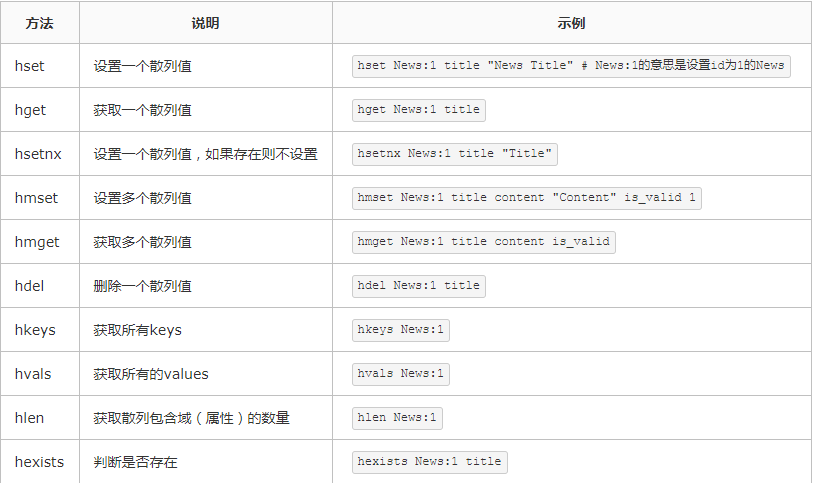
相关推荐:《Python基础教程》
python操作string
import redis
class Test_String(object):
def __init__(self):
self.r = redis.StrictRedis(host='localhost', port=6379, db=0)
def test_set(self):
"""
设置一个值
:return:
"""
res = self.r.set('user2','Joshua')
print(res)
def test_get(self):
"""
获取一个值
:return:
"""
res = self.r.get('user2')
print(res)
def test_mset(self):
"""
设置多个键值对
:return:
"""
d = {'user3': 'qi', 'user4': 'shuai'}
res = self.r.mset(d)
print(res)
def test_mget(self):
"""
获取多个键值对
:return:
"""
d = ['user3', 'user4']
res = self.r.mget(d)
print(res)
def test_del(self):
"""
删除一个键值对
:return:
"""
res = self.r.delete('user3')
print(res)
def test_incr(self):
"""
增加1
:return:
"""
res = self.r.incr('num')
print(res)
def test_decr(self):
"""
减少1
:return:
"""
res = self.r.decr('num')
print(res)
def test_append(self):
"""
添加字符串
:return:
"""
res = self.r.append('user3','qi')
print(res)
def main():
t = Test_String()
# t.test_mset()
# t.test_mget()
# t.test_del()
# t.test_set()
# t.test_get()
# t.test_incr()
# t.test_decr()
t.test_append()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()python 操作列表
import redis
class Test_List(object):
def __init__(self):
self.r = redis.StrictRedis(host='localhost', port=6379, db=0)
def test_push(self):
l_eat = ['Joshua', 'Amy']
lres = self.r.lpush('eat2', *l_eat)
print(lres)
rres = self.r.rpush('eat2', *l_eat)
print(rres)
def test_pop(self):
res = self.r.lpop('eat2')
print(res)
res = self.r.rpop('eat2')
print(res)
def test_lindex(self):
# 获取某个偏移量的值
res = self.r.lindex('eat2',0)
print(res)
def test_lrange(self):
res = self.r.lrange('eat2',0,2) # 获取某段偏移量的值
print(res)
res = self.r.lrange('eat2',0,-1) # 获取列表所有值
print(res)
def test_ltrim(self):
res = self.r.ltrim('eat2', 1,2) # 窃取一段值,其他值删除掉
print(res)
res = self.r.lrange('eat2', 0, -1)
print(res)
def test_bpop(self):
res = self.r.blpop('eat2',timeout=3) # 在3秒内从列表左端删除一个元素
print(res)
res = self.r.brpop('eat2',timeout=3) # 在3秒内从列表右端删除一个元素
print(res)
def test_rpoplpush(self):
res = self.r.rpoplpush('mylist', 'youlist') # 从mylist的右端删除一个元素,添加到youlist的最左边
print(res)
def test_brpoplpush(self):
# 从mylist的右端删除一个元素,添加到youlist的最左边,如果mylist为空则等待3秒
res = self.r.brpoplpush('mylist', 'youlist',timeout=3)
print(res)
def test_pushx(self):
# 当key存在的时候才往列表左端插入一个数据
res = self.r.lpushx('youlist', 1)
print(res)
# ~右端
res = self.r.rpushx('itslist',1)
print(res)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t = Test_List()
# t.test_push()
# t.test_pop()
# t.test_lindex()
# t.test_lrange()
# t.test_ltrim()
# t.test_blpop()
# t.test_rpoplpush()
# t.test_brpoplpush()
t.test_pushx()python操作集合
import redis
class Test_Set(object):
def __init__(self):
self.r = redis.StrictRedis(host='localhost',port=6379,db=0)
def test_sadd(self):
data = ['cat', 'dog']
res = self.r.sadd('zoo1', *data)
print(res)
res = self.r.smembers('zoo1') # 获得集合的所有元素
print(res)
def test_srem(self):
# data = ['cat', 'dog']
# res = self.r.srem('zoo', *data) # 删除多个元素
res = self.r.srem('zoo','dog') # 删除单个元素
print(res)
res = self.r.smembers('zoo')
print(res)
def test_sinter(self): # 获取两个集合的交集
res = self.r.sinter('zoo','zoo1')
print(res)
def test_sunion(self): # 获取两个集合的并集
res = self.r.sunion('zoo','zoo1')
print(res)
def test_sdiff(self): # 获取两个集合不同之处
res = self.r.sdiff('zoo','zoo1')
print(res)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t = Test_Set()
# t.test_sadd()
# t.test_srem()
# t.test_sinter()
# t.test_sunion()
t.test_sdiff()python操作散列
import redis
class Test_Hash(object):
def __init__(self):
self.r = redis.StrictRedis(host='localhost', port=6379, db=0)
def test_hset(self): # 设置一个哈希值
res = self.r.hset('News:1', 'Title', 'News Title')
print(res)
def test_hdel(self): # 删除一个哈希值
res = self.r.hdel('News:1', 'Title')
print(res)
def test_hget(self): # 获取一个值
res = self.r.hget('News:1', 'Title')
print(res)
def test_heists(self): # 判断是否存在
res = self.r.hexists('News:1', 'Title')
print(res)
def test_hgetall(self): # 获取所有哈希
res = self.r.hgetall('News:1')
print(res)
def test_hmset(self): # 设置多个哈希
data = {'content':'this is content', 'data':'20190101'}
res = self.r.hmset('News:1', data)
print(res)
def test_hmget(self): # 获取多个哈希
fields = ['content', 'data']
res = self.r.hmget('News:1',fields)
print(res)
def test_hkeys(self): # 获取所有keys
res = self.r.hkeys('News:1')
print(res)
def test_hvalues(self): # 获取所有values
res = self.r.hvals('News:1')
print(res)
def test_hlen(self): # 获取fields的数量
res = self.r.hlen('News:1')
print(res)
def test_hsetnx(self): # 设置一个哈希值,如果存在则不设置
res = self.r.hsetnx('News:1', 'content', 'fuck')
print(res)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t = Test_Hash()
# t.test_hset()
# t.test_hdel()
# t.test_hget()
# t.test_heists()
# t.test_hgetall()
# t.test_hmset()
# t.test_hmget()
# t.test_hkeys()
# t.test_hvalues()
# t.test_hlen()
t.test_hsetnx()





