import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import numpy.random as randn
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
from pylab import mpl
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 我自己配置的问题
plt.rc('figure', figsize=(10, 6)) # 设置图像大小
%matplotlib inline1. figure对象
Matplotlib的图像均位于figure对象中。
创建figure: plt.figure()
fig = plt.figure()
2. subplot子图
add_subplot:向figure对象中添加子图。
add_subplot(a, b, c):a,b 表示讲fig分割成axb的区域,c 表示当前选中要操作的区域(c从1开始)。
add_subplot返回的是AxesSubplot对象,plot 绘图的区域是最后一次指定subplot的位置
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,1) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,2) ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,3) ax4 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,4)
random_arr = randn.rand(50) # 默认是在最后一次使用subplot的位置上作图 plt.plot(random_arr,'ro--') # r:表示颜色为红色,o:表示数据用o标记 ,--:表示虚线 # 等价于: # plt.plot(random_arr,linestyle='--',color='r',marker='o') plt.show()
# hist:直方图:统计分布情况 plt.hist(np.random.rand(8), bins=6, color='b', alpha=0.3) # bins:数据箱子个数
(array([ 3., 0., 0., 0., 2., 3.]),
array([ 0.10261627, 0.19557319, 0.28853011, 0.38148703, 0.47444396,
0.56740088, 0.6603578 ]),
<a list of 6 Patch objects>)
# 散点图 plt.scatter(np.arange(30), np.arange(30) + 3 * randn.randn(30))

subplots :生成子图/子图数组
# 柱状图 fig, ax = plt.subplots() x = np.arange(5) y1, y2 = np.random.randint(1, 25, size=(2, 5)) width = 0.25 ax.bar(x, y1, width, color='r') # 画柱子ax.bar(x+width, y2, width, color='g') # 画柱子ax.set_xticks(x+width) ax.set_xticklabels(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']) # 下标注明
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex=True, sharey=True) # 共享轴坐标
subplots_adjust:调整subplots的间距
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.5,top=0.5)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2)
random_arr = randn.randn(8) fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2) axes[0, 0].hist(random_arr, bins=16, color='k', alpha=0.5) axes[0, 1].plot(random_arr,'ko--') x = np.arange(8) y = x + 5 * np.random.rand(8) axes[1,0].scatter(x, y) x = np.arange(5) y1, y2 = np.random.randint(1, 25, size=(2, 5)) width = 0.25axes[1,1].bar(x, y1, width, color='r') # 画柱子 axes[1,1].bar(x+width, y2, width, color='g') # 画柱子 axes[1,1].set_xticks(x+width) axes[1,1].set_xticklabels(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']) # 下标注明
重叠绘制
legend:显示图例
random_arr1 = randn.randn(8)
random_arr2 = randn.randn(8)
fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot(random_arr1,'ko--',label='A') ax.plot(random_arr2,'b^--',label='B') plt.legend(loc='best') # 自动选择放置图例的最佳位置

设置刻度范围:set_xlim、set_ylim
设置显示的刻度:set_xticks、set_yticks
刻度标签:set_xticklabels、set_yticklabels
坐标轴标签:set_xlabel、set_ylabe
l图像标题:set_title
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1)
ax.plot(np.random.randn(380).cumsum())
# 设置刻度范围a
x.set_xlim([0, 500])
# 设置显示的刻度(记号)
ax.set_xticks(range(0,500,100))
# 设置刻度标签
ax.set_xticklabels(['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five'],
rotation=30, fontsize='small')
# 设置坐标轴标签ax.set_xlabel('X:...')
ax.set_ylabel('Y:...')
# 设置标题
ax.set_title('Example')
3. Plotting functions in pandas
plt.close('all')
s = Series(np.random.randn(10).cumsum(), index=np.arange(0, 100, 10))
s
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1)
s.plot(ax=ax,style='ko--')
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1)
data = Series(np.random.rand(16), index=list('abcdefghijklmnop'))
data.plot(kind='bar', ax=axes[0], color='k', alpha=0.7)
data.plot(kind='barh', ax=axes[1], color='k', alpha=0.7)
df = DataFrame(np.random.randn(10, 4).cumsum(0),
columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'],
index=np.arange(0, 100, 10))
df| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -0.523822 | 1.061179 | -0.882215 | -0.267718 |
| 10 | -0.178175 | -0.367573 | -1.465189 | -1.095390 |
| 20 | 0.276166 | 0.816511 | -0.344557 | 1.297281 |
| 30 | 0.529400 | 0.159374 | -2.765168 | 1.784692 |
| 40 | -1.129003 | -1.665272 | -2.746512 | 3.140976 |
| 50 | 0.265113 | -1.821224 | -5.140850 | 2.377449 |
| 60 | -2.699879 | -3.895255 | -5.011561 | 1.715174 |
| 70 | -2.384257 | -3.480928 | -4.519131 | 2.805369 |
| 80 | -2.525243 | -3.031608 | -4.840125 | 1.106624 |
| 90 | -2.020589 | -3.519473 | -4.823292 | 0.522323 |
df.plot() # 列索引为图例,行索引为横坐标,值为纵坐标
df = DataFrame(np.random.randint(0,2,(10, 2)),
columns=['A', 'B'],
index=np.arange(0, 10, 1))
df| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 |
| 9 | 1 | 0 |
df.plot(kind='bar')
df.A.value_counts().plot(kind='bar')
df.A[df.B == 1].plot(kind='kde') df.A[df.B == 0].plot(kind='kde') # 密度图
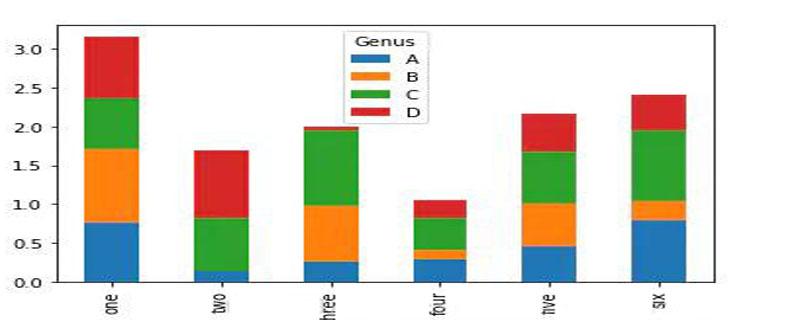
df = DataFrame(np.random.rand(6, 4),
index=['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five', 'six'],
columns=pd.Index(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], name='Genus'))
df| Genus | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| one | 0.760750 | 0.951159 | 0.643181 | 0.792940 |
| two | 0.137294 | 0.005417 | 0.685668 | 0.858801 |
| three | 0.257455 | 0.721973 | 0.968951 | 0.043061 |
| four | 0.298100 | 0.121293 | 0.400658 | 0.236369 |
| five | 0.463919 | 0.537055 | 0.675918 | 0.487098 |
| six | 0.798676 | 0.239188 | 0.915583 | 0.456184 |
df.plot(kind='bar',stacked='True') #行索引:横坐标
values = Series(np.random.normal(0, 1, size=200)) values.hist(bins=100, alpha=0.3, color='k', normed=True) values.plot(kind='kde', style='k--')
df = DataFrame(np.random.randn(10,2),
columns=['A', 'B'],
index=np.arange(0, 10, 1))
dfplt.scatter(df.A, df.B)
更多python相关文章请关注python自学网。









