Python中的while循环
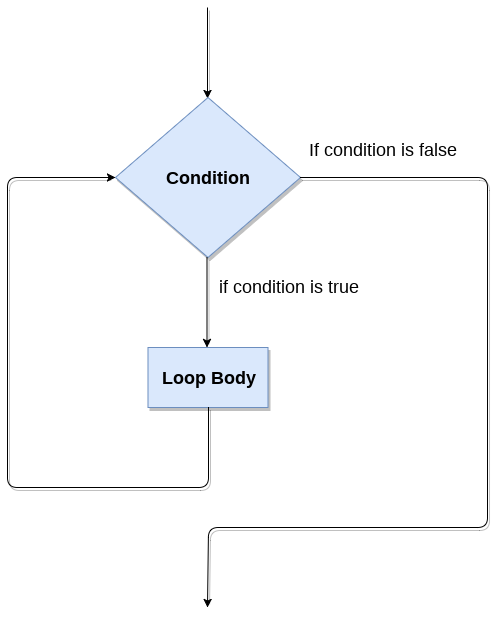
while循环也称为预测试循环。
通常,只要给定条件为真,while循环就允许执行部分代码。
它可以被视为重复的if语句。while循环主要用于事先不知道迭代次数的情况。
语法如下。
while expression: statements
这里,语句可以是单个语句或语句组。表达式应该是任何有效的python表达式,结果为true或false。true是任何非零值。
例1
i=1; while i<=10: print(i); i=i+1;
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
例2
i=1
number=0
b=9
number = int(input("输入数字?"))
while i<=10:
print("%d X %d = %d \n"%(number,i,number*i));
i = i+1;
输出:
输入数字?10 10 X 1 = 10 10 X 2 = 20 10 X 3 = 30 10 X 4 = 40 10 X 5 = 50 10 X 6 = 60 10 X 7 = 70 10 X 8 = 80 10 X 9 = 90 10 X 10 = 100
无限循环
如果while循环中给出的条件永远不会变为false,则while循环将永远不会终止并导致无限while循环。
while循环中的任何非零值表示始终为真的条件,而0表示始终为false的条件。如果我们希望程序在循环中连续运行而没有任何干扰,这种方法很有用。
例1
while (1):
print("Hi! we are inside the infinite while loop");输出:
Hi! we are inside the infinite while loop (无限循环)
例2
var = 1
while var != 2:
i = int(input("Enter the number?"))
print ("Entered value is %d"%(i))
输出:
Enter the number?102 Entered value is 102 Enter the number?102 Entered value is 102 Enter the number?103 Entered value is 103 Enter the number?103 (无限循环)
在循环中使用带有Python的else
Python使我们也可以使用while循环和while循环。当while语句中给出的条件变为false时,执行else块。与for循环类似,如果使用break语句断开while循环,则不会执行else块,并且将执行else块之后的语句。
请看以下示例:
i=1;
while i<=5:
print(i)
i=i+1;
else:print("The while loop exhausted");
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 The while loop exhausted
例2
i=1;
while i<=5:
print(i)
i=i+1;
if(i==3):
break;
else:print("The while loop exhausted");输出:
1 2





