Python的日期和时间
在现实世界的应用程序中,有些情况需要我们处理日期和时间。python中有一些例子,我们必须安排脚本在某些特定的时间运行。
在python中,日期不是数据类型,但我们可以通过导入以datetime,time和calendar命名的模块来处理日期对象。
在本教程的这一部分中,我们将讨论如何在python中使用日期和时间对象。
tick
在python中,时间瞬间从1970年1月1日上午12点开始计算。模块时间的函数time()返回自1970年1月1日上午12点以来所花费的总滴答数。刻度可以看作是最小的单位。衡量时间。
请考虑以下示例。
例
import time; #prints the number of ticks spent since 12 AM, 1st January 1970 print(time.time())
输出:
1545124460.9151757
如何获得当前时间?
time模块的localtime()函数用于获取当前时间元组。请考虑以下示例。
例
import time; #returns a time tuple print(time.localtime(time.time()))
输出:
time.struct_time(tm_year = 2018,tm_mon = 12,tm_mday = 18,tm_hour = 15,tm_min = 1, tm_sec = 32,tm_wday = 1,tm_yday = 352,tm_isdst = 0)
时间元组
时间被视为9个数字的元组。让我们看一下时间元组的成员。
| Index | Attribute | Values |
| 0 | Year | 4 digit (for example 2018) |
| Month | 1 to 12 | |
| Day | 1 to 31 | |
| Hour | 0 to 23 | |
| Minute | 0 to 59 | |
| Second | 0 to 60 | |
| Day of weak | 0 to 6 | |
| Day of year | 1 to 366 | |
| Daylight savings | -1, 0, 1 , or -1 |
获得格式化时间
可以使用time模块的asctime()函数格式化时间。它返回传递时间元组的格式化时间。
例
import time; #returns the formatted time print(time.asctime(time.localtime(time.time())))
输出:
Tue Dec 18 15:31:39 2018
Python睡眠时间
时间模块的sleep()方法用于在给定的时间内停止脚本的执行。输出将延迟指定为float的秒数。
请考虑以下示例。
例
import time for i in range(0,5): print(i) #Each element will be printed after 1 second time.sleep(1)
输出:
0 1 2 3 4
日期时间模块
datetime模块使我们能够创建自定义日期对象,在比较等日期执行各种操作。
要将日期作为日期对象使用,我们必须将datetime模块导入到python源代码中。
请考虑以下示例以获取当前时间的datetime对象表示。
例
import datetime; #returns the current datetime object print(datetime.datetime.now())
输出:
2018-12-18 16:16:45.462778
创建日期对象
我们可以通过在要为其创建日期对象的datetime构造函数中传递所需日期来创建日期对象。
请考虑以下示例。
例
import datetime; #returns the datetime object for the specified date print(datetime.datetime(2018,12,10))
输出:
2018-12-10 00:00:00
我们还可以指定时间以及创建datetime对象的日期。请考虑以下示例。
例
import datetime; #returns the datetime object for the specified time print(datetime.datetime(2018,12,10,14,15,10))
输出:
2018-12-10 14:15:10
两个日期的比较
我们可以使用比较运算符比较两个日期,例如>,> =,<和<=。
请考虑以下示例。
例
from datetime import datetime as dt
#Compares the time. If the time is in between 8AM and 4PM, then it prints working hours otherwise it prints fun hours
if dt(dt.now().year,dt.now().month,dt.now().day,8)<dt.now()<dt(dt.now().year,dt.now().month,dt.now().day,16):
print("Working hours....")
else:
print("fun hours")
输出:
fun hours
日历模块
Python提供了一个日历对象,其中包含用于处理日历的各种方法。
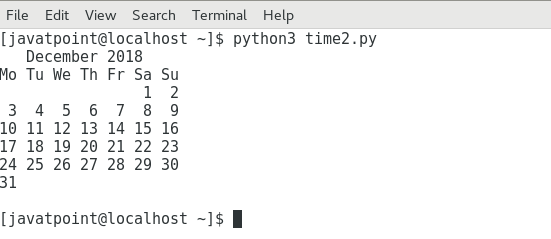
请考虑以下示例来打印2018年最后一个月的日历。
例
import calendar; cal = calendar.month(2018,12) #printing the calendar of December 2018 print(cal)
输出:
Python日期和时间
打印全年日历
日历模块的prcal()方法用于打印全年的日历。必须将要打印日历的年份传递给此方法。
例
import calendar #printing the calendar of the year 2019 calendar.prcal(2019)
输出: