
一个文件被打开后,你有一个file对象,你可以得到有关该文件的各种信息。
以下是和file对象相关的所有属性的列表:
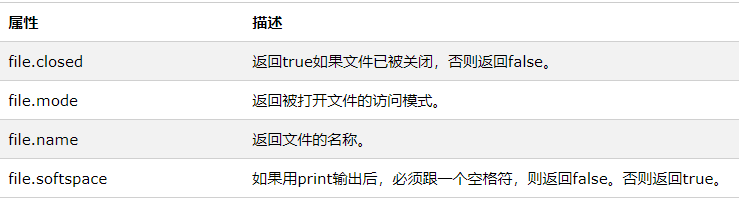
如下实例:
#!/usr/bin/python
# 打开一个文件
fo = open("foo.txt", "wb")
print "Name of the file: ", fo.name
print "Closed or not : ", fo.closed
print "Opening mode : ", fo.mode
print "Softspace flag : ", fo.softspace以上实例输出结果:
Name of the file: foo.txt Closed or not : False Opening mode : wb Softspace flag : 0
Close()方法
File对象的close()方法刷新缓冲区里任何还没写入的信息,并关闭该文件,这之后便不能再进行写入。
当一个文件对象的引用被重新指定给另一个文件时,Python会关闭之前的文件。用close()方法关闭文件是一个很好的习惯。
语法:
fileObject.close();
例子:
#!/usr/bin/python
# 打开一个文件
fo = open("foo.txt", "wb")
print "Name of the file: ", fo.name
# 关闭打开的文件
fo.close()以上实例输出结果:
Name of the file: foo.txt









